Model Answers
Q: Critically examine the dialectics involved in each mode of production as propounded by Karl Marx.
Question asked in UPSC Sociology 2021 Paper 1. Download our app for last 20 year question with model answers.
Model Answer:
Dialectics of Historical Materialism in Mode of Production
Karl Marx, a renowned philosopher, economist, and sociologist, developed a theory of historical materialism that identifies different modes of production throughout history. Each mode, according to Marx, has its own unique dialectics, or contradictions, which eventually lead to their downfall and replacement by a new mode. Here, we will critically examine the dialectics involved in each mode of production as propounded by Marx.
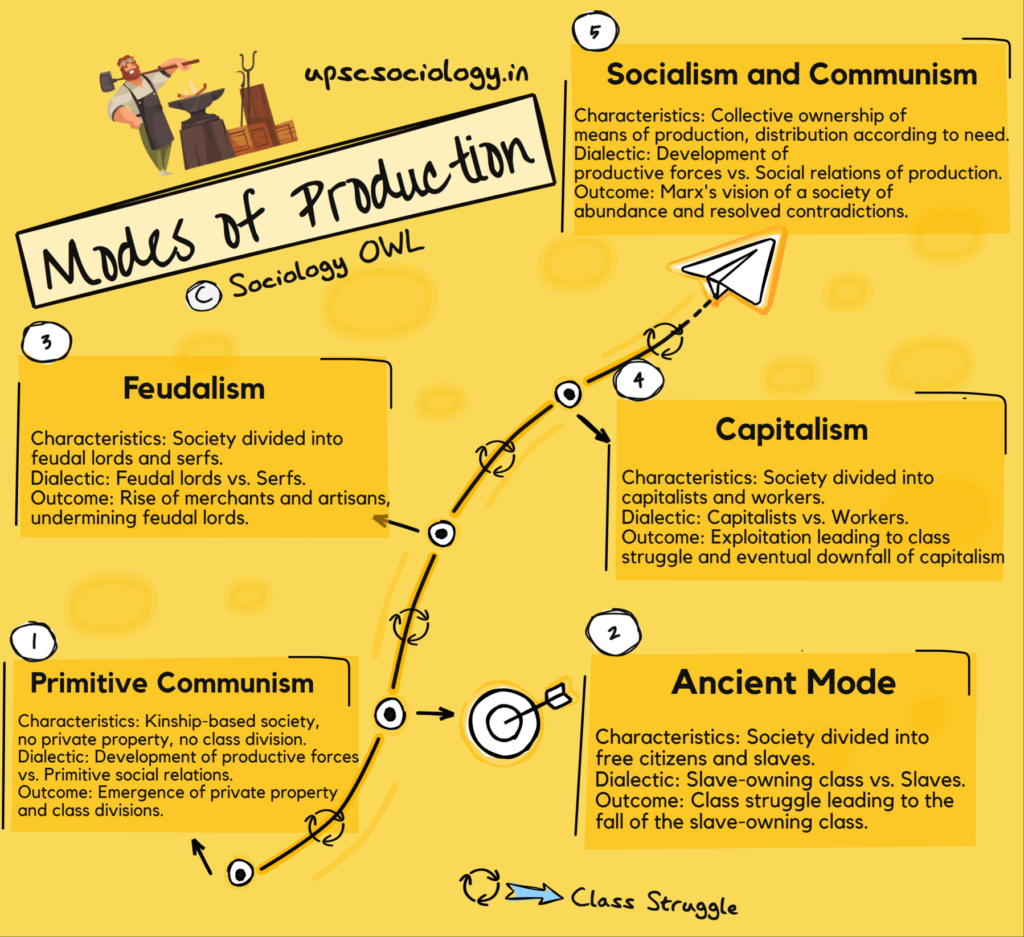
1. Primitive Communism:
This is the earliest mode of production identified by Marx. In this mode, society is organized around kinship relations, and there is no private property or class division. The dialectic in this mode is the contradiction between the development of productive forces (like tools and knowledge) and the primitive social relations of production. As productive forces develop, they eventually outgrow the communal social relations, leading to the emergence of private property and class divisions.
2. Ancient Mode:
In the ancient mode of production, society is divided into free citizens and slaves. The dialectic here is the contradiction between the slave-owning class, which controls the means of production, and the slaves, who provide the labor. This contradiction leads to class struggle and eventually the downfall of the slave-owning class.
3. Feudalism:
Feudalism is characterized by the division of society into feudal lords and serfs. The lords own the land and the serfs provide labor in exchange for protection and a portion of the harvest. The dialectic in this mode is the contradiction between the feudal lords and the serfs. The development of productive forces, like improved agricultural techniques, eventually leads to the emergence of a new class of merchants and artisans, which undermines the power of the feudal lords.
4. Capitalism:
In capitalism, society is divided into capitalists and workers. The capitalists own the means of production and the workers sell their labor in exchange for wages. The dialectic in this mode is the contradiction between the capitalists and the workers. According to Marx, the capitalists’ pursuit of profit leads them to exploit the workers, which leads to class struggle and eventually the downfall of capitalism.
5. Socialism and Communism:
Marx saw socialism and communism as the final stages of human society. In these modes, the means of production are owned collectively, and goods are distributed according to need. The dialectic in these modes, according to Marx, is the contradiction between the development of productive forces and the social relations of production. However, Marx believed that this contradiction would be resolved in communism, as the development of productive forces would eventually lead to a society of abundance, where everyone’s needs could be met.
In conclusion, Marx’s theory of historical materialism identifies a dialectic, or contradiction, in each mode of production. These contradictions lead to class struggle and eventually the downfall of each mode, paving the way for the next. This theory provides a powerful tool for understanding the dynamics of historical change and the role of class struggle in this process. However, it has been criticized for its deterministic approach and its focus on economic factors at the expense of other social, political, and cultural factors.
Download our app for UPSC Sociology Optional - Syllabus, NCERT Books, IGNOU Books, Past Paper with Model Answers, Topper Notes & Answer Sheet.