Emergence of Sociology: Origins and Development
Sociology emerged as a distinct academic discipline in 19th-century Europe in response to the major transformations of modernity. Traditional society was changing rapidly due to the decline of feudalism, the rise of capitalism, industrialization, urbanization, and political revolutions. These changes created new social problems such as inequality, class conflict, social dislocation, and weakening of traditional community ties.
At the same time, intellectual developments like the Enlightenment and the rise of scientific thinking encouraged scholars to study society through reason, observation, and evidence. As a result, sociology developed as a discipline to understand social order, social change, and modern social institutions.
How to Understand the Emergence of Sociology (UPSC Lens)
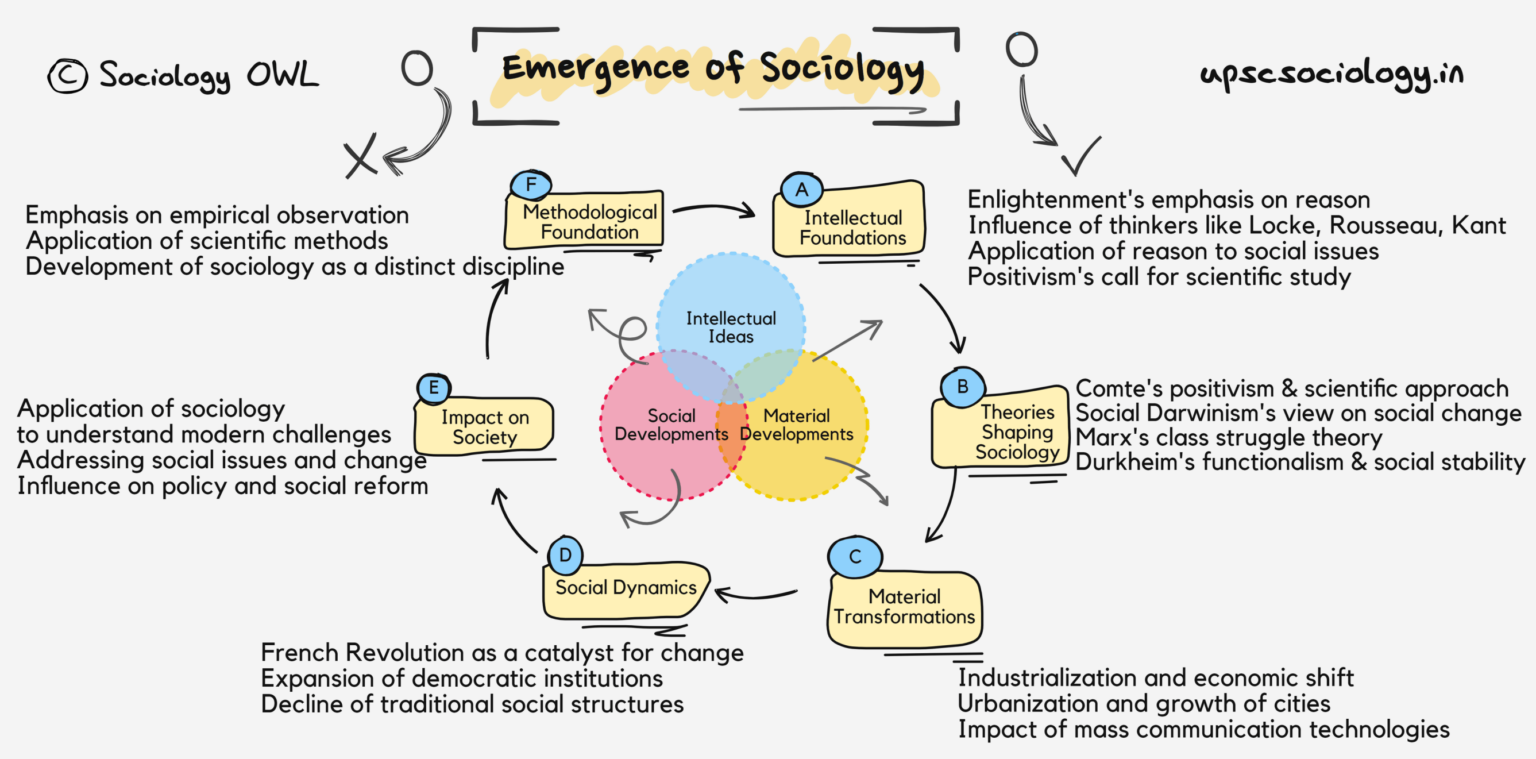
The emergence of sociology can be understood through the combined effect of intellectual developments, material-economic changes, and social-political transformations. In simple terms, modern changes in ideas, economy, and politics broke down the traditional social order and created the need to understand society scientifically.
- Intellectual developments: Enlightenment, scientific thought, positivism
- Material and economic changes: Industrialization, capitalism, urbanization
- Social and political transformations: French Revolution, decline of traditional authority
Easy recall: Modern changes in ideas + economy + politics → Breakdown of traditional order → Need to understand society scientifically → Emergence of Sociology.
1) Intellectual Background of the Emergence of Sociology
The Enlightenment: The Starting Point
The Enlightenment (17th–18th centuries) laid the intellectual foundation of sociology. It challenged blind faith in tradition and promoted the use of reason as the basis of knowledge. Thinkers of this period argued that society is made by human beings and can therefore be studied, criticized, and improved.
This was a major shift because earlier social life was often explained mainly through religion or divine will. Enlightenment thinkers changed this by treating society as something that could be understood through rational inquiry.
Important thinkers and their relevance include:
- John Locke: Emphasized individual rights and the social contract
- Rousseau: Discussed the relationship between the individual and society
- Montesquieu: Used comparison to study laws and institutions
- Immanuel Kant: Strengthened the idea of reason and critique
Because of these contributions, sociology inherited key Enlightenment assumptions: society can be studied rationally, social institutions are historically created, and social reform is possible through knowledge.
Scientific Thinking and the Rise of Positivism
The success of natural sciences influenced early sociologists. If nature could be studied scientifically, many thinkers believed society could also be studied in a similar way. This encouraged the use of observation, classification, evidence, and causal explanation in the study of society.
This scientific orientation was strongly expressed in positivism, especially in the work of Auguste Comte.
Auguste Comte and Positivism
Auguste Comte (1798–1857) is known as the father of sociology. He gave sociology its name and argued that society should be studied scientifically. Comte believed sociology should help establish order and progress in society, and this concern with both stability and change later became central to sociological theory.
Comte’s major contributions include:
- He coined the term “Sociology” in 1838
- He called sociology the “Queen of Sciences”
- He proposed the Law of Three Stages:
- Theological stage
- Metaphysical stage
- Positive (scientific) stage
Herbert Spencer and Evolutionary Thought
Herbert Spencer applied evolutionary ideas to society and compared society to a living organism. He argued that societies evolve from simple forms to more complex forms, and that social institutions become increasingly differentiated over time.
His ideas contributed to sociology by encouraging the study of long-term social change, institutional differentiation, and social evolution. Spencer also popularized the phrase “survival of the fittest”, later associated with Social Darwinism.
In UPSC answers, Spencer can be mentioned briefly as part of early evolutionary thought, with a short critical note that Social Darwinism was later criticized for being used to justify inequality, racism, and imperialism.
Karl Marx and the Conflict Perspective
Karl Marx (1818–1883) made a major contribution by placing class, conflict, and economic structures at the center of social analysis. He argued that the material conditions of life, especially the mode of production, shape social institutions, politics, and ideas.
His key concepts include:
- Historical Materialism: Economic structure influences social structure
- Class Struggle: Conflict between classes drives historical change
- Alienation: Workers become separated from their labour and human potential
- Base and Superstructure: Economy shapes law, politics, and ideology
Marx’s contribution is important because he showed that social inequality is not accidental. It is built into the structure of society, especially under capitalism. His work laid the foundation for conflict theory, critical sociology, and the study of inequality and power.
Emile Durkheim and Scientific Sociology
Emile Durkheim (1858–1917) played a decisive role in making sociology an independent academic discipline. He argued that society has a reality of its own and should be studied through specifically sociological concepts.
His most important contribution was the idea of social facts, which he defined as ways of acting, thinking, and feeling that are external to individuals and exert pressure on them.
Durkheim also developed key ideas such as:
- Division of Labour and changing forms of solidarity
- Mechanical and Organic Solidarity
- Anomie (normlessness in modern society)
- The importance of social integration and regulation
In his famous study Suicide (1897), Durkheim demonstrated that even a deeply personal act can be explained through social causes. This was a landmark moment in sociology because it proved that social phenomena can be studied scientifically.
Max Weber and Interpretive Sociology
Max Weber (1864–1920) is essential to any UPSC answer on the emergence of sociology. Weber expanded sociology beyond positivism and argued that society cannot be understood only through external facts. Sociologists must also understand the meanings people attach to their actions.
His key contributions include:
- Verstehen (interpretive understanding)
- Social Action as the central unit of analysis
- Rationalization as a defining feature of modern society
- Bureaucracy as the dominant modern organizational form
- Types of Authority:
- Traditional
- Charismatic
- Rational-legal
In The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism, Weber also showed how religion and culture can shape economic behaviour. This was important because it moved sociology beyond purely economic explanations and gave a more multidimensional understanding of modern society.
2) Material and Economic Developments Behind the Emergence of Sociology
Industrial Revolution: The Most Important Background
The Industrial Revolution was one of the strongest historical reasons for the emergence of sociology. It began in Britain in the late 18th century and transformed society from an agrarian order into an industrial-capitalist one.
This transformation led to:
- Factory-based production
- Wage labour
- Mechanization
- Large-scale economic change
- New class formations
Two new classes became especially important: the Bourgeoisie (owners of capital) and the Proletariat (industrial workers). Industrialization created new social problems such as exploitation, poverty, labour unrest, and displacement. These conditions forced thinkers to ask new questions about work, inequality, and social order.
Sociology emerged in part as an attempt to understand and explain these transformations.
Urbanization and the Changing Nature of Social Life
Industrialization led to rapid urbanization, as people moved from villages to towns and cities in search of work. This changed the nature of social life in fundamental ways.
Urban life was marked by:
- Overcrowding
- Slums and poor living conditions
- Weak kinship control
- Anonymity
- Rising crime and deviance
- Social isolation
Traditional community bonds became weaker, and new forms of association developed. These changes encouraged sociologists to study urban society, social disorganization, changing family patterns, and community life. Urbanization therefore became a central context for sociological thinking.
Capitalism and Market Society
The rise of capitalism transformed not only the economy but also social relations. Labour became a commodity, competition increased, and market logic began to influence social life more deeply.
Capitalism brought major changes such as:
- Commodification of labour
- Profit-oriented production
- Class inequality
- Individualism and competition
- Instability in livelihoods
Different sociologists responded to capitalism in different ways. Marx focused on exploitation and class conflict, Weber examined rational capitalism and work ethic, and Durkheim studied moral regulation and anomie under modern economic life.
Because capitalism reshaped institutions, relationships, and values, it became a central object of sociological analysis.
Growth of the Modern State and Bureaucracy
As modern societies developed, the state became more organized and powerful. Nation-states expanded systems of administration, law, taxation, policing, and census. This created a new kind of social order based on impersonal rules and institutional control.
The rise of bureaucratic governance led sociologists to study:
- Authority
- Organization
- Administration
- Law and legitimacy
This historical change strongly influenced Max Weber’s analysis of bureaucracy and rational-legal authority. It also helped establish sociology’s concern with institutions and power structures.
Print Culture and Public Debate
The spread of literacy and print culture also supported the emergence of sociology. Newspapers, journals, pamphlets, and books helped ideas travel quickly across society and created a wider space for public discussion.
Print culture contributed to:
- Wider access to knowledge
- Public discussion of social issues
- Critique of monarchy and Church authority
- Growth of reform and revolutionary ideas
This created an informed public sphere where social problems could be debated. Such an intellectual climate was important for the development of sociology as a discipline.
3) Social and Political Changes That Shaped Sociology
French Revolution (1789): Social Change Becomes Visible
The French Revolution had a deep impact on the emergence of sociology. It overthrew the feudal order and challenged monarchy and Church authority. It also introduced modern political ideals such as liberty, equality, fraternity, and citizenship.
The Revolution showed that society is not fixed; it can be changed through collective action. At the same time, it also produced violence, instability, and uncertainty. This raised a central question for early sociologists: How can social order be maintained in a rapidly changing society?
This question shaped the work of both Comte and Durkheim, who were deeply concerned with order, stability, and moral regulation.
Decline of Feudalism and Traditional Authority
Modernity weakened older systems of social control based on feudal hierarchy, kinship, and religion. This decline of traditional structures created greater individual freedom, but it also created uncertainty and moral fragmentation.
Important processes included:
- Decline of feudal social hierarchy
- Weakening of religious authority (secularization)
- Changing family and kinship patterns
- Rise of individualism
These shifts became major themes in sociology. Durkheim studied the crisis of moral regulation through anomie, Weber studied changing forms of authority and rationalization, and Marx studied how capitalism restructured social relations.
In short, sociology emerged because traditional society was breaking down and modern society needed explanation.
4) Conclusion
The emergence of sociology was the result of a major historical transition, not a single event or thinker. Intellectual developments such as the Enlightenment and positivism, material transformations like industrialization and capitalism, and social-political changes such as the French Revolution and secularization together created the need for a systematic study of society.
Comte, Marx, Durkheim, and Weber responded to this need in different ways, but all of them were trying to understand the same reality: the rise of modern society and its problems. For UPSC Sociology Optional, the key point is that sociology emerged as a response to the crisis and complexity of modernity. This is why sociology remains highly relevant even today, when societies continue to face inequality, institutional change, and rapid social transformation.