Model Answers
Q: What is historical materialism? Examine its relevance in understanding contemporary societies.
Question asked in UPSC Sociology 2023 Paper 1. Download our app for last 20 year question with model answers.
Model Answer:
What is Historical Materialism ?
Historical materialism is a theoretical framework developed by Karl Marx that seeks to explain social, political, and economic changes throughout history through the lens of material conditions and class struggle. This approach posits that the mode of production in a society fundamentally shapes its social, political, and ideological structures.
Key aspects of historical materialism include:
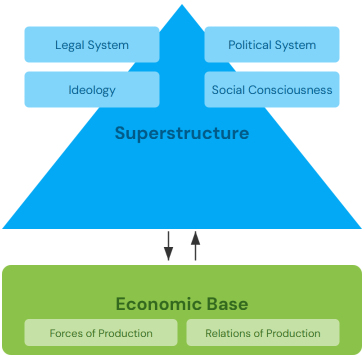
1. Economic Base and Superstructure: Marx argued that the economic base (means of production and relations of production) determines the superstructure (social, political, and ideological institutions).
2. Class Struggle: The conflict between the ruling class (bourgeoisie) and the working class (proletariat) is seen as the primary driver of historical change.
3. Dialectical Process: Social change occurs through a dialectical process of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis, leading to new stages of societal development.
4. Historical Stages: Marx identified distinct stages of historical development, including primitive communism, slavery, feudalism, capitalism, and eventually, communism.
Relevance in understanding contemporary societies:
1. Economic Determinism: Historical materialism helps explain how economic factors continue to shape social and political structures. For example, the rise of global capitalism has led to significant changes in labor markets, migration patterns, and international relations.
2. Class Analysis: The framework remains useful in analyzing class dynamics and inequalities in modern societies. The growing wealth gap and the emergence of new social classes (e.g., the precariat) can be understood through this lens.
3. Technological Change: Historical materialism can shed light on how technological advancements impact social relations and power structures. The digital revolution, for instance, has transformed labor processes and social interactions.
4. Globalization: The theory helps explain the interconnectedness of global economic systems and their impact on local cultures and societies.
5. Environmental Issues: Historical materialism can be applied to understand the relationship between capitalist production and environmental degradation.
However, critics argue that historical materialism:
1. Oversimplifies complex social phenomena by reducing them to economic factors.
2. Fails to adequately account for non-economic factors like culture, religion, and individual agency.
3. Has limited predictive power in the face of rapid technological and social changes.
In conclusion, while historical materialism has limitations, it remains a valuable tool for analyzing contemporary societies. It provides a framework for understanding the interplay between economic structures and social change, offering insights into ongoing issues of inequality, globalization, and technological transformation.
More Questions:
Download our app for UPSC Sociology Optional - Syllabus, NCERT Books, IGNOU Books, Past Paper with Model Answers, Topper Notes & Answer Sheet.


