Model Answers
Q: Bring out the various issues involved in Dalit movements in India.
Question asked in UPSC Sociology 2022 Paper 2. Download our app for last 20 year question with model answers.
Model Answer:
Dalit Movement in India
The Dalit movement in India has a long and complex history, with its roots in the caste-based social structure that has persisted for centuries. The term “Dalit” refers to the lowest castes in the Hindu caste hierarchy, who have been subjected to social, economic, and political marginalization. The Dalit movement aims to challenge and dismantle the caste system and empower the Dalit community by addressing various issues that they face.
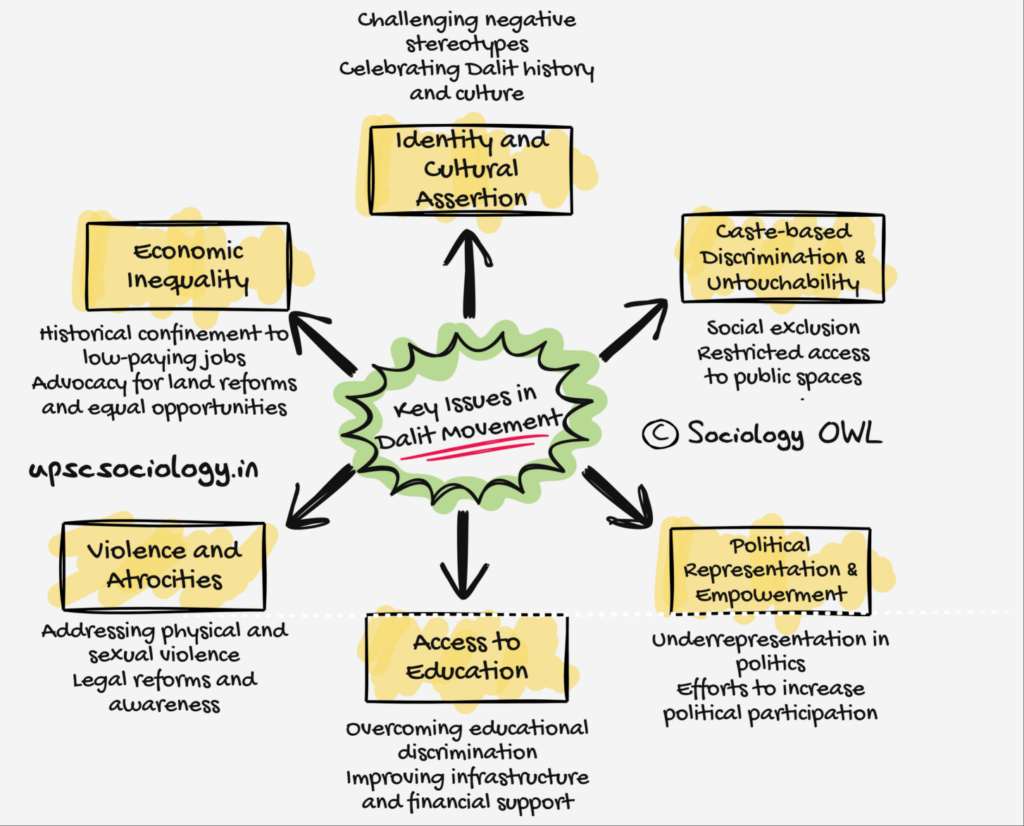
Key Issues in the Dalit Movement
1. Caste-based discrimination and untouchability: The caste system in India has led to the social exclusion and marginalization of the Dalit community. They have been subjected to untouchability, which is the practice of ostracizing a group by segregating them from the mainstream society. This has resulted in limited social interaction, restricted access to public spaces, and denial of basic human rights.
2. Economic inequality: The caste system has also led to economic disparities between different caste groups. Dalits have been historically confined to menial and low-paying jobs, which has resulted in widespread poverty and limited access to resources. The movement seeks to address this economic inequality by advocating for land reforms, equal opportunities in education and employment, and social security measures for the community.
3. Political representation and empowerment: The Dalit community has been underrepresented in the political sphere, which has hindered their ability to influence policies and decisions that affect their lives. The movement aims to increase political representation and participation of Dalits in order to empower the community and ensure that their voices are heard.
4. Access to education: Education is a crucial tool for social and economic mobility. However, the Dalit community has historically faced discrimination and exclusion in the education system, which has limited their access to quality education. The movement seeks to improve access to education for Dalits and address issues such as discrimination in schools, inadequate infrastructure, and lack of financial support for education.
5. Violence and atrocities against Dalits: The Dalit community has been subjected to various forms of violence and atrocities, including physical assault, sexual violence, and social boycotts. The movement seeks to address these issues by raising awareness, advocating for legal reforms, and providing support to victims of violence.
6. Intersectionality: The Dalit movement recognizes that the issues faced by the community are not homogenous and that there are multiple layers of discrimination and marginalization based on gender, religion, and regional identities. The movement aims to address these intersecting forms of oppression and work towards a more inclusive and equitable society.
7. Identity and cultural assertion: The Dalit movement also seeks to challenge the negative stereotypes and stigma associated with the Dalit identity and promote a positive sense of self and cultural pride. This involves reclaiming and celebrating Dalit history, art, and culture, and asserting their rights to dignity and respect.
In conclusion, the Dalit movement in India is a multifaceted struggle that seeks to address various issues faced by the community, ranging from social and economic discrimination to political representation and cultural assertion. The movement aims to dismantle the caste system and empower the Dalit community by advocating for social, economic, and political equality and justice.
More Questions:
Download our app for UPSC Sociology Optional - Syllabus, NCERT Books, IGNOU Books, Past Paper with Model Answers, Topper Notes & Answer Sheet.