Model Answers
Q: Discuss the problem of religious minorities in India and suggest measures to solve them.
Question asked in UPSC Sociology 2022 Paper 2. Download our app for last 20 year question with model answers.
Model Answer:
Religious Minorities in India: Challenges and Solutions
India’s religious diversity, as noted by T.N. Madan, presents both opportunities and challenges in maintaining social harmony. While the constitution guarantees secular principles, the reality for religious minorities is complex.
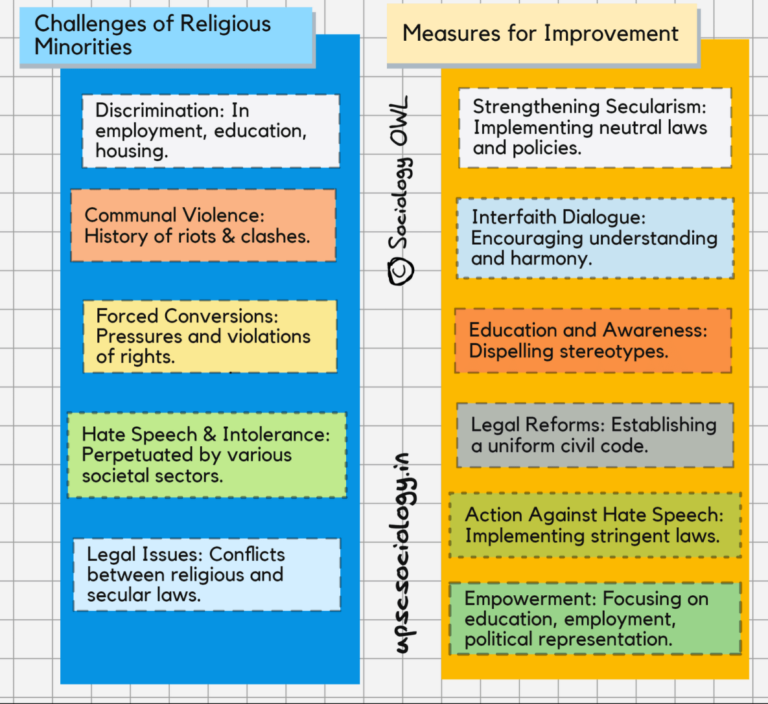
Problems faced by religious minorities:
1. Discrimination: Religious minorities frequently face discrimination in various aspects of life. For example:
– Employment: A 2019 study by Oxfam India found that Muslim job applicants were 35.3% less likely to be called for interviews compared to equally qualified Hindu candidates.
– Housing: The phenomenon of “housing apartheid” is observed in many urban areas, where minorities struggle to rent or buy properties in certain neighborhoods.
2. Communal violence: India has witnessed several instances of communal riots, such as:
– The 1984 anti-Sikh riots following Indira Gandhi’s assassination
– The 2002 Gujarat riots primarily affecting the Muslim community
– The 2008 Kandhamal riots targeting Christians in Odisha
These events not only result in loss of life and property but also create lasting fear and insecurity among minority communities.
3. Forced conversions: While illegal, instances of forced conversions still occur. For example:
– The alleged “Love Jihad” phenomenon, where Muslim men are accused of converting Hindu women through marriage
– Reports of tribal communities being coerced into converting to Christianity or Hinduism in exchange for economic benefits
4. Hate speech and intolerance: The rise of social media has amplified hate speech against minorities. For instance:
– Inflammatory speeches by political leaders during election campaigns
– Circulation of fake news and misinformation targeting specific religious groups
5. Legal issues: Conflicts between religious personal laws and secular laws create challenges. For example:
– The debate over the Uniform Civil Code and its potential impact on minority personal laws
– Issues related to religious conversion laws in various states
Measures to solve the problems faced by religious minorities:
1. Strengthening secularism:
– Implement the recommendations of the Sachar Committee Report (2006) to improve the socio-economic conditions of Muslims
– Ensure equal representation of all religions in government bodies and decision-making processes
2. Promoting interfaith dialogue:
– Establish interfaith councils at national and state levels
– Organize annual interfaith festivals celebrating the diversity of Indian religions
3. Education and awareness:
– Introduce comparative religion studies in school curricula
– Launch public awareness campaigns highlighting the contributions of different religious communities to Indian culture and history
4. Legal reforms:
– Review and amend discriminatory laws and policies
– Strengthen the National Commission for Minorities to effectively address grievances
5. Strict action against hate speech and violence:
– Implement the recommendations of the Bezbaruah Committee (2014) on combating racial discrimination
– Establish fast-track courts to deal with cases of communal violence
6. Empowerment of religious minorities:
– Increase reservation quotas for minorities in education and employment
– Provide skill development programs and financial assistance for minority-owned businesses
In conclusion, addressing the challenges faced by religious minorities in India requires a multifaceted approach. By implementing these measures and fostering a culture of inclusivity and respect, India can work towards realizing its constitutional ideal of unity in diversity.
More Questions:
Download our app for UPSC Sociology Optional - Syllabus, NCERT Books, IGNOU Books, Past Paper with Model Answers, Topper Notes & Answer Sheet.